

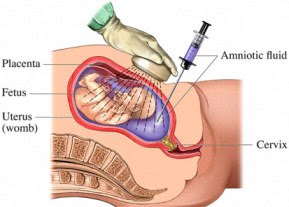
It is a technique of prenatal diagnosis performed around 16-17 wks of pregnancy. The amniotic fluid obtained contains desquamated fetal cells that can be grown in tissue culture and Karyotyped or used for metabolic assays or DNA extraction genetic evaluation.
For amniocentesis, a preliminary USG is performed to confirm gestational age, fetal number, placental localization, fetal anomaly. After painting the abdomen with iodone antiseptic, skin and subcutaneous tissues are infiltrated with local anaesthetic, the position of amniotic fluid pocket is re-confirmed and a 22gauge, 3.5 inch spinal needle is inserted under direct ultrasound visualization. The obturator is then removed, a syringe is attached to the needle and 15-20ml of amniotic fluid is withdrawn after discarding the first 0.5ml to avoid maternal blood contamination.
Chorion Villus biopsy/ sampling can be done much earlier at around 10 to 12 weeks. It can be done by transcervical insertion of sampling catheter or a transabdominal approach, both under ultrasound guidance.
Certain benign ovarian cysts (appear anechoic or black on USG with clear fluid within) can be treated as a two minute ultrasound guided aspiration procedure. Recurrent benign functional or non-functional ovarian cysts usually less than 6-7 cm in diameter can be treated this way. The Trans vaginal ultrasound probe, attached with an automated and retractable needle puncture, is introduced into the patient’s vagina. Guided by the sonographic images, the gynaecologist can advance the needle through the vaginal wall into the ovary to drain fluid from the cyst. The fluid is then collected and sent for cyto-pathology. This procedure can be done as a simple out-patient procedure without any anaesthesia.
In 30% of cases, the fluid may re-accumulate which may necessitate repetition of the procedure.
Its advantages over laparoscopic cyst removal are significantly lower cost of aspiration and the minimal recovery period after the procedure.
Chronic non-functioning follicles not responding to OCP withdrawl can be aspirated transvaginally similar to the technique of transvaginal aspiration of benign ovarian cysts. This can be done as an out-patient procedure without anaesthesia.
For ovum retrieval in IVF cycles, General anaesthesia is required and the procedure is done in IVF operation theatre. After the requisite aseptic preparation (as for any major surgery), a sterilized needle guide is attached to the probe, sterilized lubricating jelly is applied on the tip and the probe is carefully inserted into the vagina.
Multifetal pregnancy reduction is suggested with three or more fetuses present. (a common occurance with ART procedures). Multiple gestations are at higher risk of fetal, neonatal and maternal complications as well as complete pregnancy loss compared to singleton pregnancies. Selective fetal reduction is done between nine and twelve weeks (around 11 weeks) gestation and is most successful early in pregnancy. Mostly the reduction is done to two fetuses. The process is done under anaesthesia in operation theatre. A needle is inserted, either through abdomen or vagina guided by ultrasound and Potassium chloride is given to the selected fetus (es) in the heart. Usually the fetus which is lying uppermost is chosen for the procedure.
Unruptured live tubal ectopic pregnancies can sometimes be treated conservatively. Achieving asystole via sonographically guided injection of potassium chloride (KCl) along with systemic methotrexate can improve treatment outcome. Under sonographic guidance, KCl is injected into the fetal heart to achieve cardiac asystole, or systemic methotrexate is injected.
Transvaginal ultrasound guided aspiration of tubal ectopic pregnancy and instillation of hyperosmolar glucose injection with 16 gauge needle can also be performed.
Cervical ectopic pregnancy or heterotypic pregnancy (simultaneous uterine and extrauterine pregnancy) can also be treated with transvaginal ultrasound guided aspiration of ectopic and instillation of KCl or hyperosmolar glucose injection.