

The semen analysis is a very important test and should be done early in the evaluation process. If a severe sperm defect is discovered, the testing on the female partner might be modified, and therapy can be immediately directed to the sperm problem.
About 25% of all infertility is caused by a sperm defect and 40-50% of infertility cases have a sperm defect as the main cause, or a contributing cause.
Method for Collection :- Masturbation, Coitus interruptus, special condom
[No spermatocidal agents ]
Abstinence Period :- 3-4 days
Collection area :- In close proximity to the laboratory (to avoid long transport)
Container :- Big mouth polypropelene plastic jar
Aspermia: absence of semen
Azoospermia: absence of sperm
Hypospermia: low semen volume
Oligozoospermia: low sperm count
Asthenozoospermia: poor sperm motility
Teratozoospermia: sperm carry more morphological defects than usual
Necrozoospermia: all sperm in the ejaculate are dead
Anti sperm Antibodies test which determines the presence of antibodies, which immobilize or kill the sperm and prevent them swimming up towards the egg. To detect the presence of these antibodies, it is necessary to test the blood of both partners, in the cervical mucus and in the seminal fluid. Several methods are available for performing this test, which is not easy to standardize. The best method that is available presently is one that uses immunobeads. It allows the determination of the location of the antibodies on the sperm surface.
The other test is Ion -a semen culture test where the semen is tested to find the presence of bacteria.
The other sperm tests are: Postcoital Test (PCT), which is performed when the wife is in the fertile period. The Bovine Cervical Mucus Test tests for the ability of the sperm to penetrate and swim through the cervical mucus. The Sperm Survival test provides vital information on the functioning potential of the sperm.
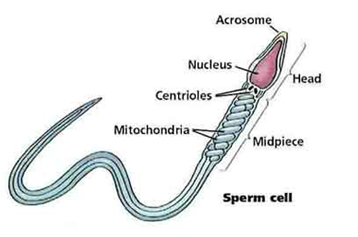
Morphology studies the size, shape and the appearance of the sperm cells. If abnormal sperm is present, there is a likelihood that the fertility is low.
WHO 2010 criteria for normal semen values
Volume = 1.5 ml or greater
pH – > 7.2
Sperm concentration = 15 million / ml
Total sperm count = 39 million / ejaculate
Motility > 4% with normal morphology
If no significant abnormality found in any parameters of spermogram proceed with further test.