


All of the blood cells in your body start out as young (immature) cells called hematopoietic stem cells. (Hematopoietic means blood-forming.) Even though they may be called “stem cells” for short, these cells are not the same as stem cells from embryos that are studied in cloning and other types of research. Here, we will use “stem cells” to mean hematopoietic stem cells.
Stem cells mostly live in the bone marrow (the spongy center of certain bones), where they divide to make new blood cells. Once blood cells are mature they leave the bone marrow and enter the bloodstream. A small number of stem cells also get into the bloodstream. These are called peripheral blood stem cells.
Stem cell transplants are used to restore the stem cells when the bone marrow has been destroyed by disease, chemotherapy (chemo), or radiation. Depending on the source of the stem cells, this procedure may be called a bone marrow transplant, a peripheral blood stem cell transplant, or a cord blood transplant. We will give you more detail on each of these later. Any of these types may be called a hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
The first successful bone marrow transplant was done in 1968. It was not until nearly 20 years later that stem cells taken from circulating (peripheral) blood were transplanted with success. More recently, doctors have begun using cord blood from the placenta and umbilical cords of newborn babies as another source of stem cells.
Stem cells make the 3 main types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
We need all of these types of blood cells to keep us alive. And in order for these blood cells to do their jobs, you need to have enough of each type in your blood.
Stem cell transplants are used to replace bone marrow that has been destroyed by disease, chemo, or radiation. In some diseases, like leukemia, aplastic anemia, certain inherited blood diseases, and some diseases of the immune system
There are 3 possible sources of stem cells to use for transplants: bone marrow, the bloodstream (peripheral blood), and umbilical cord blood from newborns. Although bone
Bone marrow is the spongy tissue in the center of bones. Its main job is to make blood cells that circulate in your body and immune cells that fight infection.
Bone marrow was the first source used for stem cell transplants because it has a rich supply of stem cells.
Normally, few stem cells are found in the blood. But giving hormone-like substances called growth factors to stem cell donors a few days before the harvest causes their stem cells to grow faster and move from the bone marrow into the blood.
Bone marrow was the first source used for stem cell transplants because it has a rich supply of stem cells.
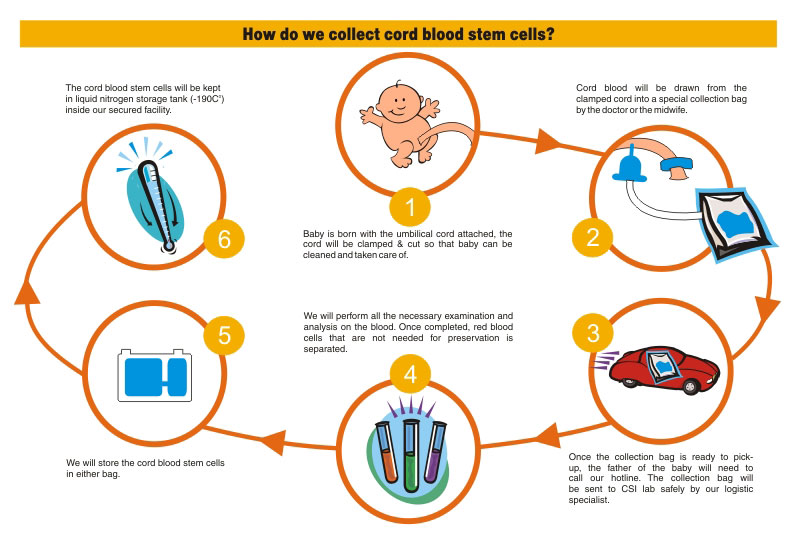
A large number of stem cells are normally found in the blood of newborn babies. After birth, the blood that is left behind in the placenta and umbilical cord (known as cord blood) can be taken and stored for later use in a stem cell transplant. The cord blood is frozen until needed.
Stem cells can be preserved for life time, but as of now, we store it for 21 years as per universal guidelines.
These stem cells are stored at a temperature of -196 degrees Celsius in vapor phase of liquid Nitrogen.
Bone marrow was the first source used for stem cell transplants because it has a rich supply of stem cells.
The total cost of stem cell preservation for 21 years is Rs 75,000.
It involves a flexibility of paying the full amount in installments.